Types of cyber risks modern Indian businesses face :
2014, Gujarat
Deepak Nitrate, a listed company in BSE with a net worth of around Rs 1,500 crore, fails to get payment for a consignment sent to a client in the US. Upon inquiry, it turns out they had deposited the money in a new account in Malaysia. But Deepak Nitrate had no such account and had no knowledge about an official mail sent from the company’s official ID regarding the same. The Gujarat Police cyber cell registered a case but the investigations have not led to any results.
2015
In this case, we can’t name the two Indian conglomerates who are the affected companies. These firms came under the attack of hackers who had got access to the system two years before this incident. The companies had to pay $5 million to stop the hackers from making public evidence of fraudulent practices.
2017
In a cyberattack, a huge sum of money gets transferred from the Union Bank of India. The bank identified the money trail and with the help of few highly placed connections and government interventions, it stopped the flow of money.
While the money involved was substantial, it also raises the question of cybersecurity in
banks, which generally employ heavier security to avoid such issues.
This is how hacking — the modern threat of malicious or criminal digital activities — has been affecting businesses. The public, the government, and not even the Indian companies have realized how big this threat is. According to reports, every third SME in India has been a victim of hacking, albeit in different degrees.
Types of Cyberattacks
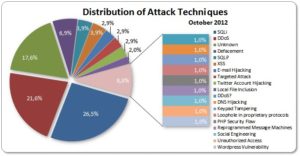
These attacks are carried out using different methodologies. The first way is phishing carried out with a high level of polish or hacking of email accounts. The other method is hacking into an establishment’s database that allows the attacker to get hold of confidential information.
8 major common cyber threats
Malware: Introduction of malicious software in the server/IT system.
Phishing: Creating a fake web page to capture sensitive data like passwords.
Password Theft: It is simply stealing the passwords to official accounts.
DDoS: The IT system is gunned down by making excessive requests to the server.
Man in the Middle: An eavesdropper intercepts communications between two legit users.
Drive-by Downloads: Malicious software is installed when the user visits a website.
Rouge Software: Posing as another legitimate software.
Malvertising: Virus/malware is installed when the user clicks on an ad.
How does a cyberattack hurt business?
In these days of start-ups, information (read, idea) is the key to success and the business is as good as gone once stolen. There are also perennial issues like a loss to finances (like the United Bank case mentioned earlier), theft of user information (for instance, Yahoo), or even personal online assets.
The other way to damage a company’s reputation is DDoS. It is the means to prove a company inefficient by repeatedly and constantly making the services offline or inaccessible.
It is the means to prove a company inefficient by repeatedly and constantly making the services offline or inaccessible.
Modern Indian businesses face a multitude of cyber risks, ranging from data breaches and ransomware attacks to social engineering and insider threats, highlighting the diverse types of cyber risks they need to address.
How to make your business’s IT systems safe?
There is a common saying among system admins and IT security professionals that “if it has an input, it can be hacked”. In other words, everything is hackable in IT. Although these threats are not common, no company’s system is forever safe or hack-proof.
The best way is to protect your business is by opting for cyber insurance. It provides exhaustive protection and/or compensation in case of these hack attacks.
These policies cover liability and property losses. In case of a data breach, the business gets cover for the loss of personal, financial, or confidential information. This policy also meets related costs like credit monitoring, notification costs, fines and penalties, and the cost of defending claims and losses incurred due to identity theft.
Some other losses covered in such policies are funds transfer loss, business interruption, cyber extortion, computer fraud, and data loss.
What makes an organization more vulnerable to cyber-attacks?
Firstly, one of the biggest problems in India is a lack of awareness. It is a standard view among insurers that there are two types of Indian companies online — those who are aware of the attacks and those who are not. The attacks are taking place in both cases.
Secondly, there are companies, even some large ones, who don’t have written down IT security methods or standards. Many of those are not even aware of the need.
Thirdly, some companies think the IT department alone can alone handle IT security. They don’t realize that the management needs to get actively involved in the strategy-making. The authorities should at least pay attention to the strategies of the IT department.
Finally, employees’ lack of interest makes it worse and almost impossible for the IT department to enforce a total lockdown. It is not possible to check each of the emails that an employee has access to and if they are clicking on links on those communications.
Hence, to zero in on a correct insurance policy you can rely on insurance advisors like SecureNow. We can help you in selecting and maintaining such policies for your business. These help protect your business against all types of cyber risks.
About The Author
Arshdeep
MBA Insurance Management
Arshdeep is a seasoned insurance expert with 7 years of experience, specializing in Cyber Risk Insurance. As a writer for SecureNow, he delivers insightful blogs and articles that demystify the complexities of cyber risk coverage. His content is designed to help businesses understand the importance of protecting against cyber threats and data breaches. With a focus on practical advice and the latest industry trends, Arshdeep empowers readers to make informed decisions about their cyber insurance needs, ensuring robust protection in an increasingly digital world.
